The evaporator in refrigeration is the core component where the magic of cooling truly happens. Found in appliances like refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners, this critical part of the cooling system plays a vital role in maintaining low temperatures by absorbing heat from the surrounding air. As a key element of the refrigeration cycle, the evaporator coil acts as a heat exchanger, turning liquid refrigerant into a gas and drawing heat away to create a chilled environment.
Whether you’re an HVAC technician, refrigeration engineer, or simply curious about how cooling technology works, understanding the evaporator in a refrigeration system is essential. In this article, we’ll explore the working principle of the evaporator, its types, functions, temperature ranges, and why it’s considered the heart of every modern refrigeration unit.
What is an Evaporator in Refrigeration?
Definition and Importance
The evaporator in refrigeration is a crucial component of any cooling system, responsible for absorbing heat from the environment and creating the cold air we rely on in refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioners. It serves as a heat exchanger, where the refrigerant—usually in low-pressure, liquid form—evaporates into a gas by drawing in heat from its surroundings.
what does an evaporator do in a refrigerator?
So, what does an evaporator do in a refrigerator? It removes heat from the inside of the refrigerator compartment, allowing it to maintain a consistently low temperature. The refrigerator evaporator typically consists of bare tube coils or plate-type surfaces that are cooled as the refrigerant flows through them, enabling effective heat transfer and efficient cooling.
In the case of the evaporator in AC (air conditioner) units, the principle remains the same. The evaporator absorbs heat from the indoor air, which is then blown over the evaporator coils by a fan. As the refrigerant evaporates inside the coil, it cools the air, which is then circulated back into the room—creating a refreshing, comfortable environment.
Overall, whether in a domestic freezer, central air conditioning system, or commercial refrigeration unit, the evaporator plays a key role in the refrigeration cycle, making it an essential component in modern HVAC and cooling technologies.
Differance Between Evaporator and Condenser
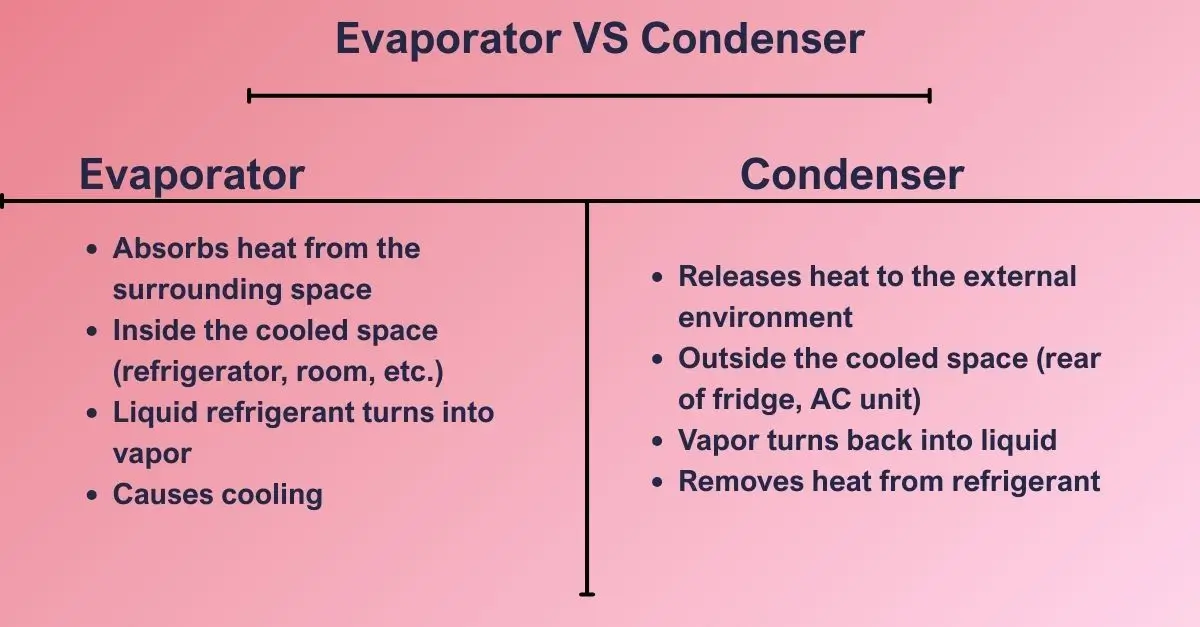
In any refrigeration system or air conditioner, both the evaporator and condenser play essential but opposite roles in the refrigeration cycle. Understanding the difference between an evaporator and a condenser helps in grasping how a cooling system functions effectively.
How Does an Evaporator Work?
The evaporator is the part of the refrigeration cycle where the actual cooling process takes place. It acts as a heat exchanger, absorbing heat from the surrounding environment and allowing the refrigerant to evaporate inside the coil. This phase change from liquid to vapor is the key mechanism that cools the air in a refrigerator, freezer, or air conditioner.
🔄 Step-by-Step Working of an Evaporator:
-
Low-Pressure Refrigerant Enters the Coil:
-
After passing through the expansion valve, the refrigerant enters the evaporator coil as a low-pressure, cold liquid.
-
-
Heat Absorption Begins:
-
The refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding air, food items (in a refrigerator), or indoor air (in an AC). As it absorbs heat, it begins to boil and evaporate, turning from a liquid to a vapor.
-
-
Air Flows Over the Evaporator Coil:
-
A fan blows warm air across the evaporator coils, where the heat is transferred from the air to the refrigerant. This results in the air being cooled and circulated back into the cooling system (fridge or room).
-
-
Vapor Moves to the Compressor:
-
The now warm, low-pressure refrigerant vapor moves to the compressor, which starts the next phase of the refrigeration cycle.
-
Types of Evaporators in Refrigeration Systems
Evaporators come in different designs to suit various cooling applications, environments, and performance requirements. Each type plays a similar role—absorbing heat through the refrigeration cycle—but differs in design, installation style, and energy efficiency.
Below are the four most commonly used evaporators in modern refrigeration systems:
1️⃣ Bare Tube Evaporator
The bare tube evaporator is one of the simplest forms of evaporators used in refrigeration systems. It consists of plain metal tubes through which the refrigerant flows, absorbing heat from the surrounding air or surface. Due to the absence of fins, it has a lower heat transfer efficiency but offers ease of cleaning and maintenance, making it ideal for applications like cold storage rooms and walk-in freezers where frequent defrosting or moisture accumulation occurs. It’s best suited for environments where air circulation is forced or natural.
-
Common Use: Cold storage rooms, walk-in freezers, and industrial applications
-
Advantage: Easy to clean and maintain
-
Limitation: Lower heat transfer rate compared to finned designs
2️⃣ Plate Type Evaporator
The plate type evaporator features two flat metal plates sealed together with refrigerant channels in between, offering a large surface area for heat exchange in a compact design. These evaporators are commonly found in domestic refrigerators and freezers, especially where food or products are in direct contact with the cooling surface. Known for their efficient thermal conductivity and space-saving construction, plate evaporators are widely used in small-scale applications where direct cooling is necessary, and airflow is limited.
-
Common Use: Domestic refrigerators, freezers
-
Advantage: Excellent surface contact with stored items; compact size
-
Limitation: Less effective in large-scale applications
3️⃣ Finned Tube Evaporator
The finned tube evaporator enhances heat transfer by attaching thin metal fins to the tube surface, significantly increasing the surface area for better air contact. It is highly efficient and widely used in air conditioners, display freezers, and bottle coolers. The fins allow for faster and more uniform cooling by improving the airflow across the evaporator coil. However, these evaporators require regular cleaning, as dust and debris buildup on the fins can reduce performance over time. Despite this, they are preferred in air-based cooling systems for their high efficiency.
-
Common Use: Air conditioners, display freezers, bottle coolers
-
Advantage: High efficiency; ideal for air-based cooling
-
Limitation: Prone to dust accumulation; needs regular cleaning
4️⃣ Shell and Tube Type Evaporator
The shell and tube evaporator is a heavy-duty design mainly used in industrial refrigeration and HVAC chillers. It consists of a cylindrical shell filled with refrigerant and a bundle of tubes carrying water or another fluid. Heat exchange takes place indirectly, making this design highly efficient and suitable for large-scale operations with high cooling demands. Although more expensive and bulky than other evaporators, its durability, reliability, and ability to handle large refrigerant volumes make it the top choice for commercial and industrial settings.
-
Common Use: Centralized AC systems, chillers, industrial refrigeration
-
Advantage: Durable, suitable for large cooling loads
-
Limitation: Expensive and bulky
Components of an Evaporator
An evaporator comprises several components that facilitate heat transfer between the refrigerant and the environment. These components include:
- Refrigerant inlet and outlet
- Evaporator housing
- Expansion valve
- Capillary tube
- Fins or tubes
- Drain pan
Forced Convection vs. Natural Convection Types
The evaporator in refrigeration can also be classified based on airflow mechanism:
-
Forced Convection Evaporators: Use a fan to push air across the evaporator coil, ensuring uniform and faster heat absorption. Commonly found in air conditioners and modern refrigerators.
-
Natural Convection Evaporators: Rely on natural air movement for heat exchange. These are more energy-efficient but slower in performance, often used in basic refrigeration units.
Choosing the right type of evaporator in refrigeration depends on system needs such as cooling speed, energy consumption, and design constraints.
What Does the Evaporator Do in a Refrigerator vs. an AC?
Though both refrigerators and air conditioners rely on evaporators to provide cooling, the way they function within each system varies slightly based on application, design, and airflow. Let’s explore their distinct roles:
🧊 1. Role of the Evaporator in a Refrigerator
In a refrigerator, the evaporator is usually located at the back or top of the cooling compartment or freezer section. The refrigerant enters the evaporator coil as a cold, low-pressure liquid. As warm air from inside the fridge passes over the coils, the refrigerant absorbs the heat and evaporates, cooling the surrounding air.
🔍 Real-Life Example:
Imagine opening your domestic freezer on a hot day—notice how cold air rushes out? That chilled air is the result of heat being constantly removed from the inside compartment by the refrigerator evaporator, keeping your food fresh and frozen.
🌬️ 2. Role of the Evaporator in an Air Conditioner
In an air conditioning unit, the evaporator in AC is typically located inside the indoor unit (also called the air handler). It cools the indoor air by absorbing heat through the evaporator coil. As the air conditioner pulls in warm air from your room, the air passes over the cold coils, where the refrigerant inside evaporates and absorbs the heat. The cooled air is then circulated back into the room.
🔍 Real-Life Example:
When you switch on your split AC or window AC, within minutes you feel a noticeable drop in room temperature. That comfort is brought to you by the evaporator in AC, silently absorbing indoor heat and pushing cool air back through your vents.
🌡️ Evaporator Temperature & Performance Factors
The evaporator temperature plays a vital role in determining how efficiently a refrigeration system or air conditioner can cool. Whether in a domestic freezer, refrigerator, or AC unit, keeping the evaporator operating within the ideal temperature range ensures consistent cooling, energy savings, and long-term system health.
✅ Normal Temperature Range of an Evaporator
In most refrigeration systems, the evaporator coil typically operates at temperatures around 0°F (-18°C) or even lower—especially in freezers. In air conditioning systems, the evaporator temperature usually ranges between 35°F to 45°F (1.7°C to 7.2°C). If the temperature drops too low, it may cause ice to form on the coils, while a higher temperature may reduce cooling efficiency.
⚠️ Key Factors That Affect Evaporator Performance
-
Airflow Obstruction:
Poor airflow across the evaporator coil, due to a blocked fan or dirty air filters, reduces heat absorption, leading to insufficient cooling and possible coil freezing. -
Dirt and Dust on Coils:
A dirty evaporator surface acts as insulation, reducing the heat exchange process. This forces the system to work harder, increasing energy use and wear. -
Refrigerant Level Issues:
Low or excessive refrigerant levels can disturb the evaporation process. Too little refrigerant leads to higher temperatures and less cooling, while overcharging can damage the compressor. -
Thermostat Malfunction:
A faulty thermostat may fail to regulate temperature correctly, causing the evaporator to run too cold or not cool enough. -
Improper Defrost Cycle:
In domestic freezers, if the defrost cycle is not working properly, frost or ice can accumulate on the evaporator, reducing its ability to absorb heat.
🛠️ Tips to Maintain Evaporator Efficiency
-
✅ Clean the Evaporator Coils Regularly: Remove dirt, dust, and frost buildup to allow proper heat exchange.
-
✅ Check and Replace Filters: Ensure air filters in AC units are clean to maintain proper airflow.
-
✅ Monitor Refrigerant Levels: Have a technician inspect and recharge the system as needed.
-
✅ Inspect Airflow Paths: Ensure nothing blocks the airflow over the evaporator, like clutter in refrigerators or vents in ACs.
-
✅ Schedule Preventive Maintenance: Regular servicing keeps all components—including the evaporator in AC and refrigerator evaporator—running smoothly.
By monitoring evaporator temperature and addressing the performance factors above, you can dramatically improve the cooling capacity and energy efficiency of your refrigeration system or air conditioning unit
⚠️ Common Problems in Evaporators & Troubleshooting Tips
Over time, the evaporator in your refrigerator or air conditioner may develop issues that affect its performance. If not addressed early, these problems can lead to poor cooling, system inefficiency, or even complete failure of your cooling system. Below are some of the most frequent evaporator problems and how to troubleshoot them effectively.
❄️ 1. Ice or Frost Buildup on Evaporator Coils
Cause:
This is a common issue in domestic freezers and AC units, often caused by restricted airflow, a faulty defrost timer, or low refrigerant levels.
Symptoms:
-
Reduced cooling performance
-
AC or fridge running continuously
-
Ice forming on the coils or rear wall of the refrigerator
Troubleshooting Tips:
-
Ensure air vents are not blocked
-
Check and replace dirty air filters in AC units
-
Inspect and repair the defrost system in refrigerators
-
Call a technician to check refrigerant levels
🌀 2. Poor Airflow Across the Evaporator
Cause:
Clogged filters, a malfunctioning fan motor, or obstructions around the evaporator coil can restrict airflow, leading to inefficient cooling.
Symptoms:
-
Uneven cooling
-
Weak airflow from AC vents
-
Warm spots in the refrigerator
Troubleshooting Tips:
-
Clean or replace AC filters
-
Check for fan operation and ensure proper air circulation
-
Avoid overpacking the refrigerator, which restricts internal airflow
⚙️ 3. Leaking or Damaged Evaporator Coil
Cause:
Wear and tear or corrosion can cause tiny holes or cracks in the evaporator coil, leading to refrigerant leakage.
Symptoms:
-
Hissing sounds
-
Weak cooling despite the system running
-
Ice forming only on parts of the coil
Troubleshooting Tips:
-
Look for oily residue near coils (a sign of refrigerant leak)
-
Call a professional to conduct a leak test and recharge refrigerant
-
Replace the coil if damage is severe
📉 4. Evaporator Not Reaching Correct Temperature
Cause:
A malfunctioning thermostat, faulty sensor, or insufficient refrigerant can prevent the evaporator from reaching the desired evaporator temperature.
Symptoms:
-
Items in the fridge aren’t cold enough
-
AC struggles to cool the room
-
System short-cycles (turns on and off quickly)
Troubleshooting Tips:
-
Test and calibrate the thermostat
-
Clean the evaporator coil
-
Schedule professional HVAC or appliance servicing
🧊 5. Strange Noises from the Evaporator Area
Cause:
Fan blades hitting ice or debris, a faulty motor, or refrigerant hissing through a tiny leak.
Symptoms:
-
Clicking, buzzing, or whistling noises
-
Intermittent cooling
-
AC or refrigerator runs louder than normal
Troubleshooting Tips:
-
Check for ice buildup near the fan
-
Ensure nothing is physically obstructing the coil or fan blades
-
Listen for persistent sounds and report them to a technician
✅ Summary of Evaporator Troubleshooting
| Problem | Possible Cause | Quick Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Frost buildup | Low refrigerant, airflow issue | Clean filters, check refrigerant level |
| Weak airflow | Blocked vents, dirty filters | Unblock airflow, replace filters |
| Leaking coil | Corrosion, wear and tear | Call technician for leak detection |
| Uneven cooling | Faulty thermostat | Test or replace temperature sensor |
| Strange noises | Fan obstruction or ice buildup | Defrost and inspect fan area |
🏭 Applications of Evaporators in Various Industries
The evaporator is a key component in many modern systems where temperature control, cooling efficiency, and heat absorption are vital. From preserving food to maintaining sterile environments in hospitals, evaporators are widely used across multiple industries. Here’s a look at how different sectors benefit from evaporator technology.
🌬️ 1. HVAC Industry
In the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) industry, the evaporator coil is essential for indoor cooling. Found in split ACs, central air conditioning systems, and window units, the evaporator in AC absorbs heat from indoor air and releases cool air into the living or working space. It’s crucial for maintaining comfort in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
✅ Example:
Modern office buildings use centralized air conditioning systems with large evaporator coils to maintain optimal temperatures for employees.
🧊 2. Food Storage & Preservation
The food industry relies heavily on evaporators for cold storage, freezers, walk-in coolers, and refrigerated transport. In these systems, the evaporator helps maintain precise low temperatures needed to preserve food freshness, prevent bacterial growth, and extend shelf life.
✅ Example:
Supermarkets and grocery stores use evaporator coils in display freezers to keep frozen foods at consistent sub-zero temperatures.
🏗️ 3. Industrial Refrigeration Systems
In large-scale operations such as manufacturing plants, cold chains, and breweries, industrial evaporators are used in shell and tube systems or ammonia-based cooling plants. These are designed to handle high loads and maintain stable cooling over long periods, ensuring process consistency.
✅ Example:
A beverage manufacturing plant may use large evaporator units to keep raw materials and finished products at controlled temperatures during production.
🧪 4. Medical & Chemical Sectors
In the medical and chemical industries, evaporators are used to regulate temperatures in pharmaceutical storage, vaccine refrigeration, chemical labs, and clean rooms. They help maintain strict environmental conditions to protect sensitive substances from spoilage, degradation, or contamination.
✅ Example:
Hospitals use medical-grade refrigeration systems with evaporators to safely store temperature-sensitive drugs and blood plasma.
Steps to Maintain an Evaporator in Refrigeration
Proper evaporator coil cleaning should be part of every routine HVAC or refrigeration system checkup. Here are the recommended steps:
-
Turn Off the Power: Always disconnect the power supply to the refrigeration unit before starting maintenance.
-
Remove Debris and Dust: Use a soft brush or vacuum to clean surface dirt from the coils.
-
Apply a Coil Cleaner: Use a non-acidic, no-rinse evaporator coil cleaner for deep cleaning. Spray and allow it to soak.
-
Rinse with Water (if required): If the cleaner requires rinsing, use low-pressure water to wash off the residue.
-
Check the Drain Pan and Lines: Ensure there’s no blockage or mold buildup in the condensate drain.
-
Inspect for Damage or Corrosion: Check the coil and surrounding parts for any signs of wear or refrigerant leaks.
-
Restart the System: Once everything is dry and reassembled, reconnect power and test the system.
❓ FAQs About Evaporators
🔹 What is the purpose of an evaporator in a refrigeration system?
A: The evaporator absorbs heat from the surrounding environment using low-pressure refrigerant. It is the part of the refrigeration system where the refrigerant evaporates into gas, cooling the inside of the refrigerator or air conditioning unit.
🔹 How does an evaporator differ from a condenser?
A: The evaporator removes heat by absorbing it into the refrigerant, while the condenser releases that absorbed heat outside the system. Simply put, the evaporator cools, and the condenser warms.
🔹 What happens if the evaporator coil freezes?
A: A frozen evaporator coil usually indicates poor airflow, dirty filters, or low refrigerant levels. This can reduce cooling performance and increase energy consumption. Regular maintenance helps prevent this issue.
🔹 Where is the evaporator located in an air conditioner?
A: In a typical split AC system, the evaporator coil is located inside the indoor unit. It cools the room by absorbing heat from the air blown over it by a fan.
🔹 Can a faulty evaporator cause poor cooling?
A: Yes. If the evaporator in AC or a refrigerator is damaged, blocked, or leaking refrigerant, it won’t be able to absorb heat efficiently, resulting in inadequate cooling or temperature fluctuations.
🔹 How often should an evaporator coil be cleaned?
A: It’s recommended to clean evaporator coils at least once or twice a year, especially in dusty environments. Regular cleaning ensures efficient heat exchange and extends the system’s lifespan.
🔹 What types of evaporators are used in industrial settings?
A: Industrial systems often use shell and tube evaporators, which are designed to handle high cooling loads in manufacturing, cold storage, or large-scale refrigeration applications.
🔹 Is the evaporator the same in both refrigerators and AC units?
A: While the function is similar—heat absorption—the design and placement of evaporators vary between refrigerators, freezers, and air conditioning units, based on airflow and application needs
Informative
Conclusion
Final Summary & Key Takeaways
The evaporator is undeniably one of the most vital components in any refrigeration or air conditioning system. As the core part of the cooling cycle, the evaporator’s main function is to absorb heat from the surrounding air or stored items, allowing the refrigerant to evaporate and produce the desired cooling effect.
From domestic refrigerators and freezers to air conditioning units and industrial cooling systems, evaporators play a central role in regulating temperature, preserving food, maintaining indoor comfort, and ensuring the smooth operation of sensitive medical or chemical processes.
Whether it’s the evaporator in an AC unit cooling your home or a plate-type evaporator in your fridge keeping your groceries fresh, this component ensures energy-efficient, reliable, and consistent performance across all modern cooling systems.
🔑 Key Takeaways:
-
The evaporator functions as a heat absorber in the refrigeration cycle.
-
It is essential in appliances like refrigerators, freezers, AC units, and chillers.
-
Proper maintenance of the evaporator coil, refrigerant levels, and airflow is critical for system performance.
-
Understanding evaporator types and their applications helps in choosing the right cooling solution for any industry