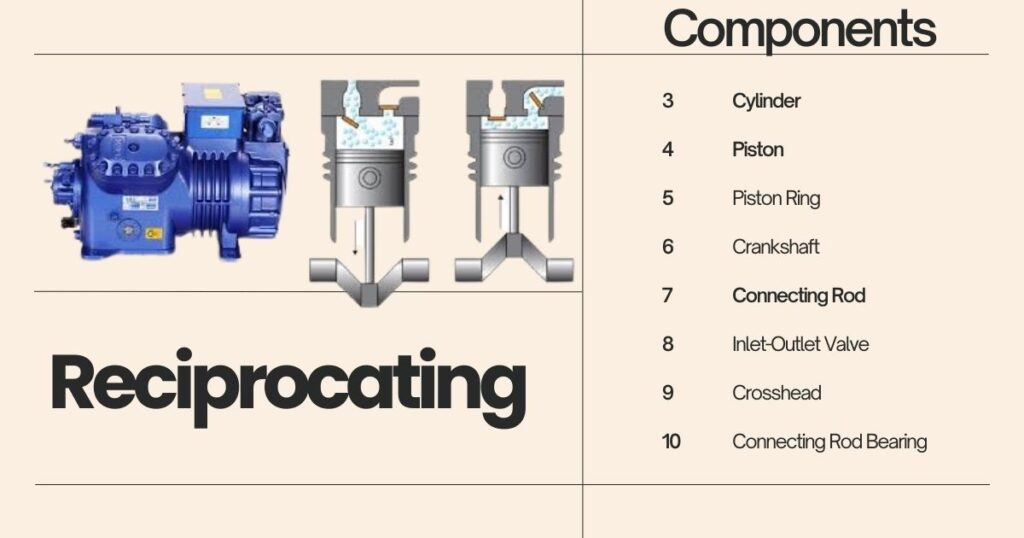
What is a Reciprocating Compressor?
A reciprocating compressor is a type of positive displacement compressor that uses a piston to compress gas. Widely used in various industries, this type of compressor is known for its efficiency and reliability in applications that require high pressure. This article explores the working principles, advantages, applications, and maintenance tips for reciprocating compressors, helping you understand their role in HVAC systems and beyond.
How Does a Reciprocating Compressor Work?
The primary working principle of a reciprocating compressor involves a piston moving inside a cylinder. As the piston moves down, it creates a vacuum that draws gas into the cylinder. When the piston moves up, it compresses the gas, increasing its pressure before it is discharged. This process is repeated in cycles, making the reciprocating compressor highly efficient for high-pressure applications.
Advantages of Reciprocating Compressors in HVAC Systems
Reciprocating compressors offer several advantages, especially in HVAC systems:
- High Efficiency: These compressors are capable of achieving high pressures, making them ideal for air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
- Reliability: Their robust design ensures long-term reliability, even under demanding conditions.
- Versatility: Reciprocating compressors can handle a variety of gases, making them suitable for multiple applications.
Reciprocating Compressor vs. Rotary Compressor
When comparing reciprocating compressors to rotary compressors, several factors come into play:
- Pressure Capability: Reciprocating compressors are better suited for high-pressure applications, whereas rotary compressors are more efficient at low to moderate pressures.
- Maintenance: Reciprocating compressors generally require more maintenance due to the moving parts, but they offer superior performance in certain applications.
- Cost: While reciprocating compressors may have a higher upfront cost, their long-term efficiency can lead to cost savings.
Applications of Reciprocating Compressors in Industry
Reciprocating compressors are used in a wide range of industries:
- Petrochemical Industry: For compressing natural gas and other gases.
- Manufacturing: To power pneumatic tools and equipment.
- HVAC Systems: For air conditioning and refrigeration applications.
- Automotive Industry: In vehicle air conditioning systems.
Reciprocating Compressor Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of reciprocating compressors is crucial for ensuring their longevity and efficiency. Here are some key maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspection: Conduct regular inspections to identify wear and tear on moving parts.
- Lubrication: Ensure proper lubrication of all moving parts to reduce friction and prevent overheating.
- Filter Cleaning: Clean or replace air filters regularly to prevent contaminants from entering the compressor.
- Pressure Monitoring: Monitor the pressure levels to ensure they remain within the recommended range.
Reciprocating Compressor Efficiency Improvement Methods
Improving the efficiency of a reciprocating compressor can lead to significant energy savings. Some methods include:
- Using Variable Speed Drives (VSDs): VSDs allow the compressor to operate at different speeds, depending on the demand, reducing energy consumption.
- Optimizing the Cooling System: Ensuring the cooling system is working efficiently can prevent overheating and improve overall performance.
- Upgrading Components: Replacing worn-out components with high-efficiency alternatives can enhance the compressor’s performance.
Common Issues with Reciprocating Compressors and Solutions
Despite their reliability, reciprocating compressors can encounter several issues:
- Valve Failure: Caused by wear and tear, leading to reduced efficiency. Solution: Regularly inspect and replace valves as needed.
- Overheating: Can occur due to insufficient lubrication or a malfunctioning cooling system. Solution: Ensure proper lubrication and check the cooling system regularly.
- Leakages: Air or gas leaks can reduce the compressor’s efficiency. Solution: Inspect and repair any leaks promptly.
Types of Reciprocating Compressors in Mechanical Engineering
Reciprocating compressors come in various types, each suited for specific applications:
- Single-Acting Compressors: Compress gas on one side of the piston only.
- Double-Acting Compressors: Compress gas on both sides of the piston, offering higher efficiency.
- Diaphragm Compressors: Use a flexible diaphragm instead of a piston, ideal for compressing toxic or hazardous gases.
Best Practices for Operating a Reciprocating Compressor
To ensure optimal performance of a reciprocating compressor, follow these best practices:
- Operate Within Recommended Limits: Always operate the compressor within the manufacturer’s recommended pressure and temperature limits.
- Regular Maintenance: Adhere to a strict maintenance schedule to prevent breakdowns and extend the compressor’s lifespan.
- Training for Operators: Ensure that all operators are properly trained in the use and maintenance of the compressor.
Energy Consumption of Reciprocating Compressors in Factories
Energy consumption is a critical factor in the operation of reciprocating compressors, especially in industrial settings. While these compressors are efficient, they can consume a significant amount of energy, especially if not properly maintained. Implementing energy-saving measures, such as regular maintenance, upgrading components, and using VSDs, can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Conclusion
Reciprocating compressors are essential components in various industries, offering high efficiency, reliability, and versatility. By understanding how these compressors work, their advantages, and how to maintain them, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity. Whether you’re using a reciprocating compressor in an HVAC system or an industrial application, following the best practices outlined in this article will help you get the most out of your equipment.