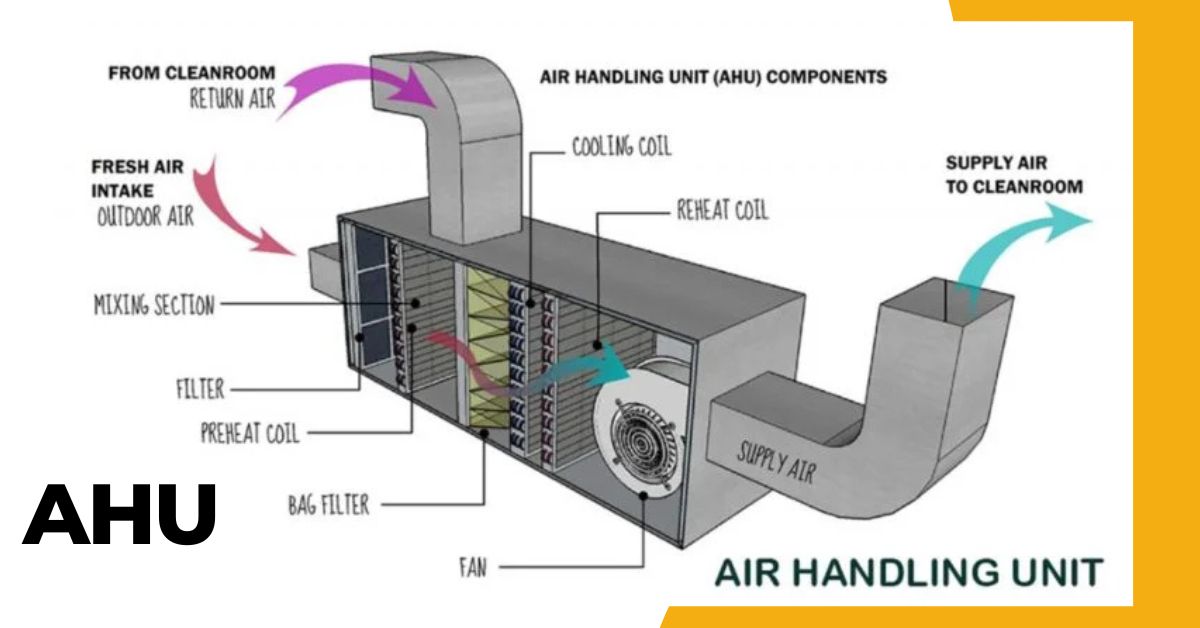
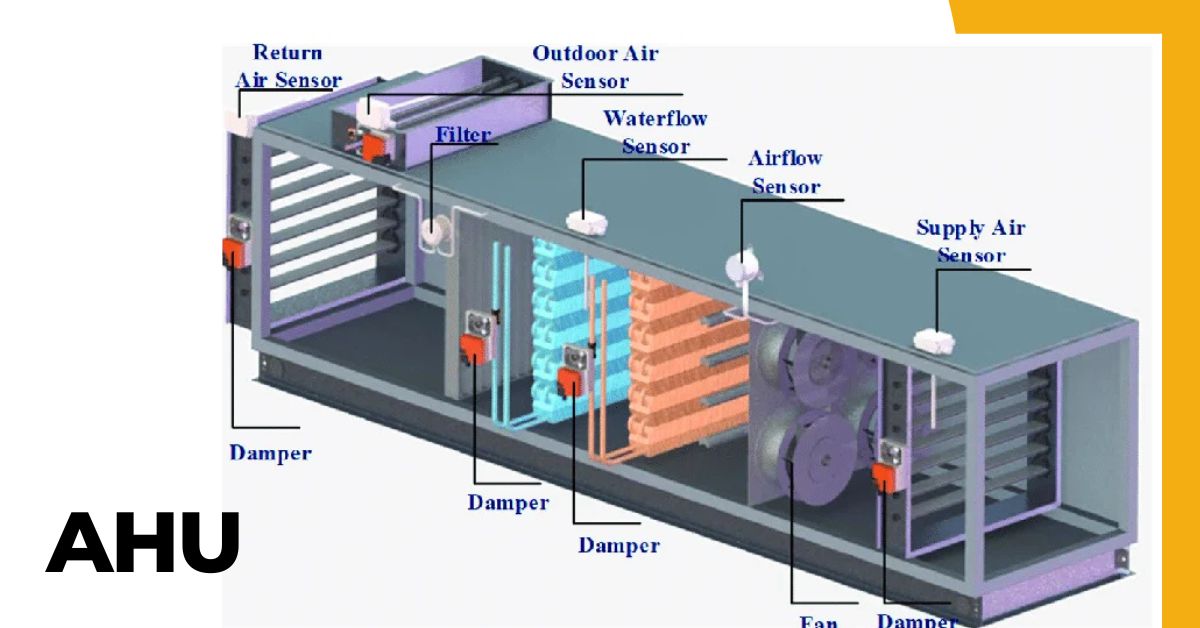
Have you ever wondered how large buildings like malls, hospitals, and offices maintain a comfortable and fresh indoor environment throughout the day? The answer lies in a vital component of HVAC systems called the Air Handling Unit (AHU).
An AHU is a central device in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, designed to regulate and circulate air for optimal indoor comfort. Its primary function is to clean, cool, heat, or humidify air before distributing it across the building. Whether it’s ensuring a healthy environment, maintaining the perfect temperature, or enhancing overall air quality, the AHU plays a critical role in making indoor spaces more livable and efficient.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the question, “What is AHU in HVAC?” We’ll explore its working mechanism, importance, types, and how it integrates into the broader HVAC system to ensure the best indoor air quality and comfort.
What is AHU in HVAC System?
AHU and HVAC Full Form
AHU stans for Air Handling Unit it is a device used in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems to manage and regulate indoor air. It is primarily responsible for circulating and conditioning the air within a building to ensure a clean, comfortable, and temperature-controlled environment. AHUs are commonly found in commercial, industrial, and large residential spaces, and they play a vital role in maintaining good indoor air quality.
Importance of AHU in HVAC Systems
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) plays a crucial role in any HVAC system by regulating and conditioning the air in a building. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it ensures a comfortable and healthy indoor environment, which is essential for the well-being of occupants and the efficiency of a building’s operations. Here’s why AHUs are indispensable in HVAC systems:
1. Maintaining Indoor Air Quality
One of the primary functions of an AHU is to filter and clean the air before circulating it throughout the building. AHUs typically contain filters that trap dust, allergens, pollutants, and other harmful particles, providing clean, breathable air. This is especially important in spaces like hospitals, offices, and factories where air quality can directly impact health and productivity.
2. Temperature Control
AHUs are equipped with heating and cooling coils that regulate the temperature of the air. Whether it’s cooling air in the summer or heating it in the winter, AHUs help maintain the desired temperature in different areas of a building. This is essential for comfort and helps optimize energy use, reducing heating and cooling costs.
3. Humidity Regulation
AHUs can also manage humidity levels within a building by using humidifiers or dehumidifiers. Proper humidity control prevents issues like mold growth and discomfort from excessively dry or damp air, making AHUs critical for maintaining a balanced indoor environment.
4. Energy Efficiency
Modern AHUs are designed with energy efficiency in mind. They often feature components like heat recovery systems, which recycle energy from exhaust air to pre-condition incoming air, reducing the need for additional heating or cooling. This makes AHUs essential for achieving energy savings in large buildings and minimizing environmental impact.
5. Ventilation and Fresh Air Supply
In addition to circulating indoor air, AHUs bring in fresh outdoor air, which is crucial for proper ventilation. This ensures that the air inside a building remains fresh and doesn’t become stale or toxic. Proper ventilation is particularly important in areas with high occupancy, like schools and office buildings, where the air quality can quickly degrade without adequate airflow.
Components of an Air Handling Unit (AHU)
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is made up of several essential components that work together to provide clean, comfortable, and well-regulated air within a building. Below are the key components of an AHU:
Filters
Filters are one of the most important parts of an AHU, as they clean the air by trapping dust, dirt, pollen, bacteria, and other pollutants. By filtering out contaminants, AHUs ensure that the air circulated in the building is fresh and healthy. There are different types of filters used in AHUs, such as:
- Pre-filters: These capture large particles like dust and dirt.
- HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters: These are designed to trap smaller particles, providing higher air quality, often used in hospitals and clean rooms.
- Carbon filters: These remove odors and gases from the air.
Fans
Fans are responsible for circulating the air through the AHU and into the ductwork that distributes the air throughout the building. They move both fresh outdoor air and conditioned indoor air, ensuring proper ventilation. Fans come in different types, such as:
- Centrifugal fans: These are commonly used in AHUs to move large volumes of air.
- Axial fans: These are used in smaller AHUs and are often more energy-efficient.
Cooling and Heating Coils
Cooling and heating coils are used to regulate the temperature of the air. These coils are connected to the building’s chilled water system or hot water system:
- Cooling coils: These remove heat from the air and lower the temperature, typically using chilled water or refrigerant.
- Heating coils: These raise the temperature of the air, usually with hot water or electric heating elements, to ensure indoor comfort during colder months.
Dampers
Dampers are mechanical devices that control the flow of air within the AHU. They are used to regulate the amount of fresh outdoor air brought into the system and to control the airflow between different parts of the HVAC system. Dampers can be used to:
- Modulate airflow: Adjust the amount of air passing through the system.
- Control air intake: Ensure that the AHU is receiving the correct amount of fresh air from outside.
- Prevent backflow: Stop air from flowing in the wrong direction.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall efficiency and effectiveness of an AHU. By working together, they help ensure that the air inside a building is well-filtered, properly circulated, and maintained at a comfortable temperature and humidity level.
Air Handling Unit (AHU) Diagram
AHU Working Principle in HVAC System
What is the Function of Air Handling Unit?
The Air Handling Unit (AHU) is a key component in HVAC systems, performing several essential functions to maintain a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Below are the main functions of an AHU:
1. Air Circulation
The AHU’s primary function is to circulate air throughout a building. This involves both the recirculation of indoor air and the intake of fresh outdoor air. The unit uses fans to push the air through the system, ensuring that it reaches all areas of the building via ducts. This process helps maintain good ventilation, especially in larger spaces like office buildings, hospitals, and malls.
2. Air Filtration
AHUs are equipped with filters that remove dust, dirt, allergens, and other pollutants from the air before it is distributed inside the building. This improves air quality and prevents respiratory issues among occupants. Depending on the requirements, filters may range from basic mesh filters to advanced HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, which trap even the smallest particles.
3. Temperature Control (Heating and Cooling)
AHUs help regulate indoor temperatures by conditioning the air. The system has cooling coils to lower the temperature of the air during hot weather and heating coils to raise the temperature during colder months. By adjusting the air temperature as it circulates, AHUs ensure comfort for building occupants, regardless of the season.
4. Humidity Control
In addition to temperature regulation, AHUs also play a role in controlling the humidity levels inside a building. Using built-in dehumidifiers or humidifiers, AHUs maintain a balanced moisture level in the air. Proper humidity control is essential for preventing mold growth, protecting sensitive equipment, and maintaining overall comfort.
5. Ventilation
Ventilation is a critical function of AHUs. The unit brings in fresh outdoor air and mixes it with indoor air, ensuring proper air exchange. This is important for removing carbon dioxide and other indoor pollutants while replacing them with oxygen-rich air. Proper ventilation is especially vital in environments with high occupancy or where pollutants are generated, such as hospitals or manufacturing facilities.
6. Energy Efficiency and Heat Recovery
Modern AHUs are designed to be energy-efficient, incorporating systems like heat recovery to minimize energy waste. Heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) or energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) capture the heat from outgoing air and use it to precondition incoming fresh air. This reduces the need for additional heating or cooling, improving the overall energy efficiency of the HVAC system.
Related Topics
What is the Difference Between AHU and HVAC?
The terms Air Handling Unit (AHU) and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) are often used in the context of indoor climate control, but they refer to different aspects of air management systems. Here’s a breakdown of their key differences:
Definition
- AHU (Air Handling Unit): An AHU is a specific piece of equipment within an HVAC system. It is responsible for conditioning and circulating air throughout a building. It mainly handles air filtration, temperature control, humidity control, and ventilation within the system.
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): HVAC refers to the entire system that provides heating, ventilation, and air conditioning to a building. It includes a combination of components like AHUs, chillers, boilers, ductwork, thermostats, and more, working together to regulate air temperature, humidity, and quality.
Role and Function
- AHU: The AHU’s primary function is to treat and circulate air. It filters, cools or heats the air, and ensures proper airflow to different parts of the building. It mainly focuses on the ventilation and conditioning of air.
- HVAC: HVAC is the complete system that includes multiple components working together. It provides heating, cooling, and ventilation throughout the building. While the AHU is an important part of the HVAC system, HVAC also includes other systems like chillers, furnaces, and air conditioning units.
Components
- AHU: A typical AHU consists of several components like fans, filters, heating/cooling coils, humidifiers/dehumidifiers, and dampers. These components work together to condition and circulate air.
- HVAC: HVAC is made up of a variety of components, including the AHU, chillers for cooling, boilers for heating, ductwork for air distribution, thermostats for temperature control, and sometimes energy recovery systems for efficiency.
Size and Complexity
- AHU: Typically, AHUs are large units installed in commercial and industrial buildings. They are one component of the overall HVAC system.
- HVAC: HVAC systems can be complex and involve multiple interconnected components. HVAC includes not only the AHU but also other critical systems, such as heating units, cooling units, and air filters, working in harmony.
What is the Difference Between AHU and FAHU?
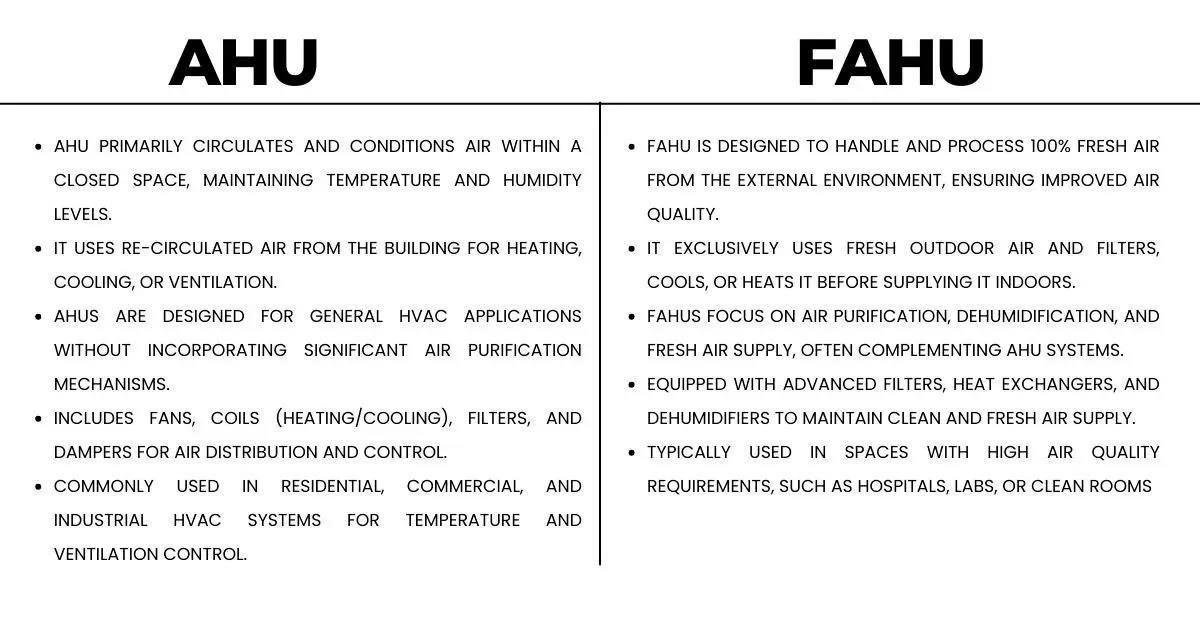
While both AHU (Air Handling Unit) and FAHU (Fresh Air Handling Unit) are components used in HVAC systems, they serve slightly different purposes and are designed to handle different types of air. Below are the key differences:
Function and Purpose
- AHU (Air Handling Unit): The AHU is responsible for conditioning and circulating air throughout a building. It can handle both recirculated indoor air and fresh outdoor air, depending on the system’s requirements. AHUs are equipped to filter, heat, cool, and circulate air to maintain the desired indoor air quality and comfort.
- FAHU (Fresh Air Handling Unit): The primary role of a FAHU is to introduce and condition fresh outdoor air into the HVAC system. FAHUs focus mainly on ventilating and supplying fresh air to the system, often for buildings that require high ventilation rates (like hospitals or industrial settings). FAHUs typically don’t handle recirculated air as AHUs do.
Air Source
- AHU: AHUs can handle both recirculated indoor air and fresh air from the outside. The fresh air intake is often mixed with the return air (recirculated air) before being treated and distributed throughout the building.
- FAHU: FAHUs are specifically designed to treat only fresh air. They ensure a constant supply of clean, outdoor air, which is especially important in environments that require high ventilation and low indoor air pollutants.
Usage
- AHU: AHUs are commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings where both recirculated and fresh air are required. These units maintain air quality, regulate temperature, and ensure overall comfort.
- FAHU: FAHUs are typically used in areas where the ventilation of fresh air is crucial, such as hospitals, laboratories, factories, or any location that needs a high volume of fresh air to meet specific air quality standards.
Air Treatment
- AHU: AHUs are equipped to treat both fresh and return air. They usually have filters, heating and cooling coils, and sometimes humidifiers or dehumidifiers to manage temperature and humidity in the air.
- FAHU: FAHUs are usually designed to only filter and condition fresh air coming from outside. They may not always have the same level of complex air treatment that AHUs have, as their main function is ensuring that fresh air is properly introduced into the system.
Energy Efficiency
- AHU: Because AHUs often mix return air with fresh air, they can be more energy-efficient in maintaining indoor air quality, as they don’t rely entirely on conditioning outdoor air, which can be more demanding.
- FAHU: FAHUs are designed to bring in large volumes of outdoor air, which means they can require more energy to condition that air, particularly if the external air temperature or humidity is very different from the desired indoor conditions.
What Are the Different Types of AHU?
Air Handling Units (AHUs) come in different types based on their design, purpose, and capacity. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
Modular AHU
- Description: Modular AHUs are built from pre-fabricated sections that can be customized and expanded as needed. This makes them highly versatile and scalable.
- Applications: Used in commercial buildings where flexibility in size and capacity is required. Ideal for facilities that may need future expansions.
Packaged AHU
- Description: A packaged AHU comes as a single, pre-assembled unit, including all necessary components (filters, fans, coils, etc.). These units are designed to be installed as-is, without the need for on-site assembly.
- Applications: Suitable for buildings with limited space or when quick installation is essential. Common in smaller commercial setups.
Custom AHU
- Description: These are specifically designed and built to meet the unique requirements of a particular building or facility. Custom AHUs offer high flexibility in terms of components and configuration.
- Applications: Used in large commercial or industrial applications where specific conditions must be met (such as custom air filtration or specific temperature control).
Single-Duct AHU
- Description: A single-duct AHU is designed to supply conditioned air through a single ductwork system. It typically includes components like a filter, fan, and cooling or heating coils.
- Applications: Ideal for systems where only one air distribution duct is needed, such as in smaller buildings or spaces with simpler HVAC requirements.
Dual-Duct AHU
- Description: Dual-duct AHUs have two separate ducts: one for cold air and one for hot air. These ducts mix inside the AHU to provide air at the desired temperature.
- Applications: Used in larger buildings with varying temperature needs in different zones, such as office buildings or hospitals.
Draw-Through AHU
- Description: In a draw-through AHU, the air is drawn through the filter, then the fan, and finally through the cooling or heating coils. The fan is located downstream of the coils.
- Applications: Used in applications where the fan’s ability to push air through filters and other components is needed. Typically found in industrial settings.
Blow-Through AHU
- Description: The fan in a blow-through AHU is positioned before the coils. This type of unit blows air through the filters, cooling coils, and heating coils.
- Applications: Preferred in systems where airflow needs to be pushed through components more efficiently, like in larger commercial facilities.
Vertical AHU
- Description: Vertical AHUs are designed with vertical airflow, meaning air moves up and down within the unit. They are typically installed where horizontal space is limited.
- Applications: Often used in buildings where space constraints demand vertical units, such as in hotels or high-rise buildings.
Horizontal AHU
- Description: Horizontal AHUs, as the name suggests, are designed for horizontal airflow. These units are installed in large spaces where they can span across walls or ceilings.
- Applications: Common in industrial or large commercial buildings where floor space is available for horizontal placement.
- Air Handling Unit Diagram
Advantages of Air Handling Units (AHUs)
Air Handling Units (AHUs) offer several significant advantages that improve the performance and efficiency of HVAC systems, making them essential for maintaining comfort and air quality in various types of buildings. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Improve Indoor Air Quality
AHUs play a crucial role in improving indoor air quality (IAQ) by filtering out dust, allergens, and other airborne pollutants before they circulate in the building. The built-in filters in AHUs trap particles like dirt, bacteria, and smoke, which ensures that only clean, filtered air is supplied to the space. This is particularly important in environments like hospitals, office buildings, schools, and commercial spaces where clean air is essential for the health and comfort of occupants.
2. Energy-Efficient Solutions for Ventilation
One of the major advantages of AHUs is their ability to optimize energy use. AHUs can incorporate energy-saving technologies such as energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery wheels, which capture heat from exhaust air and use it to pre-condition incoming fresh air. This reduces the need for additional heating or cooling and helps to lower energy costs. Furthermore, AHUs with variable speed fans adjust their speed depending on the air demand, which leads to better energy efficiency.
3. Customizable for Various Environments
AHUs are highly customizable to suit the specific needs of different environments. They can be tailored to handle varying air volumes, temperature ranges, and filtration requirements. Whether it’s a small office, a large industrial plant, or a hospital with strict air quality requirements, AHUs can be designed with specific components like filters, coils, fans, and dampers to meet the particular demands of the building. This flexibility ensures that AHUs can be adapted for a wide range of applications, ensuring optimal performance in different settings.
Conclusion
Air Handling Units (AHUs) are essential components in HVAC systems, playing a key role in ensuring optimal indoor air quality and maintaining comfort. By conditioning and circulating both fresh and recirculated air, AHUs regulate temperature, humidity, and air cleanliness, making them vital for the health and well-being of building occupants. Additionally, they offer energy-efficient solutions, reducing operating costs through features like energy recovery systems. The versatility of AHUs allows them to be customized for various environments, from residential spaces to large industrial facilities. Understanding what an Air Handling Unit is and how it functions helps in choosing the right AHU for your specific needs, ensuring both comfort and sustainability in building management.