The compressor is an essential component of air conditioning systems. They are responsible for compressing refrigerant gas and moving it through the air conditioning air conditioning system, where it cools and condenses into a liquid. In this article, we will take a closer look at compressors and how they work.
What is a Compressor?
A compressor is a device that compresses gas to increase its pressure and temperature. In air conditioning systems, compressors are typically located in the outdoor unit of a split-system air conditioner or central air conditioning system. They are powered by electricity and consist of several components, including a motor, a piston or scroll, and a valve.
The motor is responsible for driving the piston or scroll, which compresses the refrigerant gas. The valve is responsible for controlling the flow of refrigerant through the compressor. Compressors are designed to work with specific types of refrigerants, and it is important to ensure that the correct refrigerant is used in an air conditioning system to ensure optimal performance.
Compressors used in air conditioning systems
There are two main types of compressors used in air conditioning systems: reciprocating compressors and rotary compressors. Additionally, when it comes to how they compress refrigerant gas, Reciprocating compressors use pistons to compress refrigerant gas, while rotary compressors use rotating blades to compress refrigerant gas. In terms of performance, Rotary compressors are generally more efficient and produce less noise than reciprocating compressors.
In addition to their type, compressors are also classified based on their capacity, or the amount of refrigerant gas they can compress per unit of time. This is typically measured in tons or BTUs (British Thermal Units) per hour. Larger air conditioning systems require compressors with higher capacities to ensure that they can effectively cool and dehumidify indoor air.
Overall, compressors play a critical role in the operation of air conditioning systems. It is important to properly maintain and repair compressors as needed to ensure that air conditioning systems function effectively and efficiently. Regular maintenance tasks such as cleaning the compressor, checking refrigerant levels, and replacing worn components can help extend the lifespan of compressors and ensure optimal performance. Additionally, it is important to work with a qualified HVAC professional for any repairs or replacements to ensure that the air conditioning system is functioning safely and effectively.
Types of Compressor
-
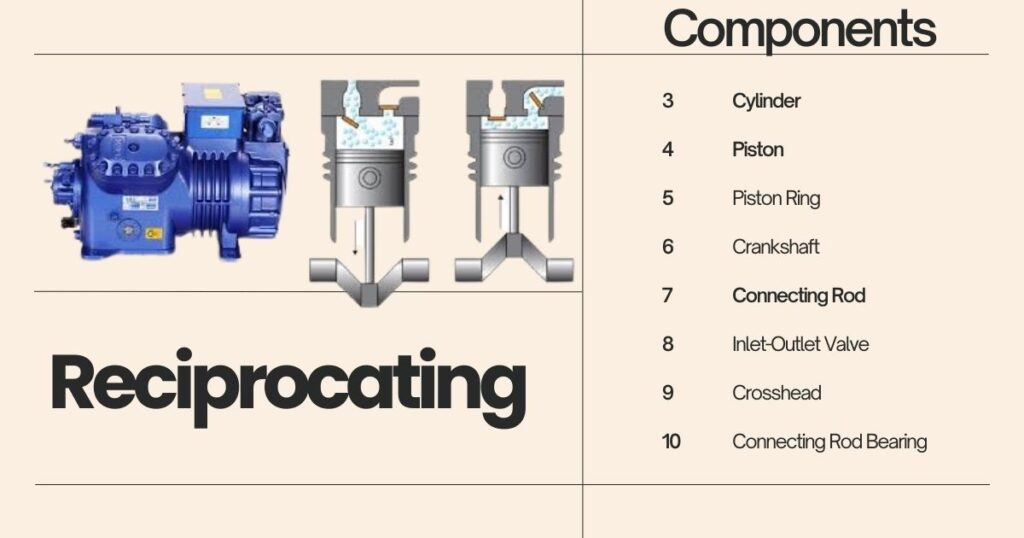
Reciprocating Compressors Reciprocating compressors are the most common type of compressor used in residential and light commercial air conditioning systems. They use a piston and cylinder to compress refrigerant gas and are available in both single and double-acting models. Reciprocating compressors are generally reliable and cost-effective but can be noisy and have a shorter lifespan than other types of compressors.
- Rotary Compressors Rotary compressors use a rotating component, typically a blade or roller, to compress refrigerant gas. They are quieter and more compact than reciprocating compressors and can handle larger capacities. However, they are typically more expensive and may require more maintenance.
- Scroll Compressors Scroll compressors use two spiral-shaped scrolls to compress refrigerant gas. They are generally more reliable and quieter than reciprocating compressors and are often used in high-end residential and commercial air conditioning systems. However, they can be more expensive and have a lower capacity than other types of compressors.
- Screw Compressors Screw compressors use two interlocking screws to compress refrigerant gas. They are typically used in larger air conditioning systems and industrial applications, where high capacity and reliability are important. However, they can be more expensive and require more maintenance than other types of compressors.
-
Centrifugal Compressors Centrifugal compressors use a spinning impeller to compress refrigerant gas. They are typically used in large commercial and industrial air conditioning systems and are known for their high capacity and efficiency. How, they are also the most expensive type of compressor and require specialized maintenance and repair.
Components of Compressor
A compressor is a device that has several components that work together to compress gases or air. Some of the key components of a compressor include:
-
Motor: The motor powers the compressor and drives the piston or impeller.
- Compressor housing: This is the outer casing of the compressor that encloses the internal components.
- Intake valve: The intake valve is responsible for allowing gas or air to enter the compressor.
- Piston or impeller: The piston or impeller is the component that compresses the gas or air by reducing its volume.
-
Compression chamber: This is the space within the compressor where gas or air is compressed.
- Discharge valve: The discharge valve is responsible for releasing compressed gas or air from the compressor.
-
Oil lubrication system: Many compressors require oil to lubricate the internal components and reduce friction.
-
Cooling system: Compressors generate a lot of heat during operation, so many models include a cooling system to prevent overheating.
-
Control system: Some compressors include a control system that regulates the flow of gas or air and ensures that the compressor operates efficiently.
Applications of Compressors
Compressors are used in many different industries and applications. Some of the most common include:
- Air conditioning units
- Refrigeration units
- Power tools
- Spray painting equipment
- Gas turbines
- Oil refineries
- Chemical processing plants
Common Faults of Compressor
While compressors are designed to be reliable and long-lasting, they can still experience faults or malfunctions from time to time. Some of the most common faults of compressors include:
1. Overheating:
Compressors generate heat during operation, and if the cooling system fails or is insufficient, the compressor can overheat and fail.
2. Oil leaks:
Many compressors require oil to lubricate the internal components, and if there is a leak in the oil system, it can lead to reduced efficiency or even failure.
3. Valve failure:
Valves in a compressor can become worn or damaged over time, which leads to reduced performance or even complete failure.
4. Piston or impeller damage:
The piston that compresses the gas can become worn or damaged, resulting in reduced performance or even complete failure.
5. Electrical faults:
The motor and electrical components in a compressor can experience faults or malfunctions, leading to reduced efficiency or even complete failure.
6. Contamination:
Contaminants such as dust, dirt, or moisture can enter the compressor and cause damage to the internal components or reduce the efficiency of the compressor.
7. Improper installation or operation:
Incorrect installation or operation of the compressor can lead to damage or failure, as well as reduced efficiency.
To prevent these faults and ensure optimal performance, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance and operation procedures. This may include regular inspections and maintenance of key components, as well as proper installation and operation of the compressor. Additionally, operators should be aware of the signs of potential faults or malfunctions, such as unusual noises, reduced performance or leaks, and take corrective action as needed.
Conclusion
Compressors are an essential part of many different industries, and they play a critical role in everything from air conditioning units to oil refineries. By compressing gas or air, these devices make it possible to store and use these resources more efficiently. Whether you’re using a power tool or enjoying the cool air from your air conditioning unit, you have a compressor to thank for making it all possible.