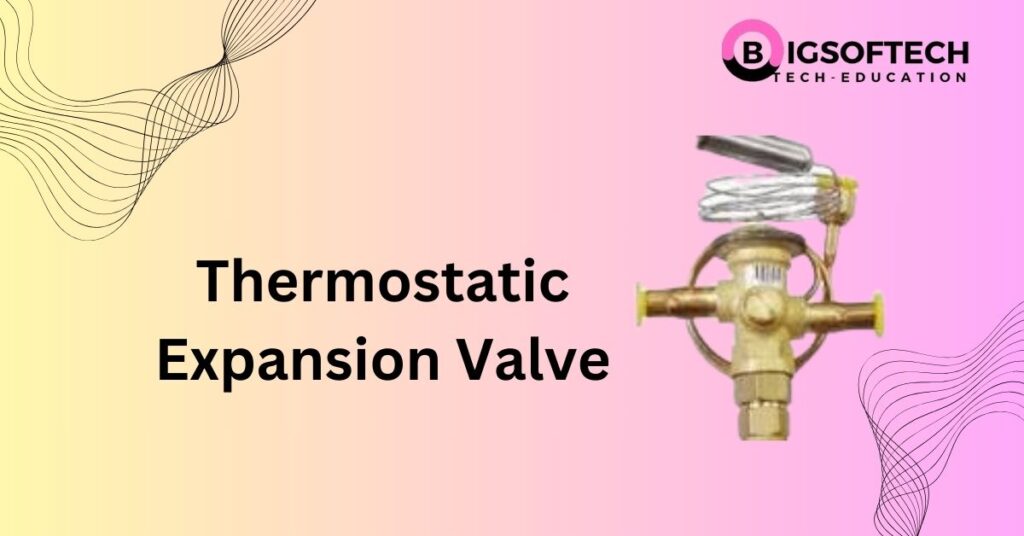
In HVAC systems, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency is crucial. One component that plays a key role in regulating the refrigerant flow in these systems is the Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV). This article will delve into everything you need to know about TXVs, from their working principles to troubleshooting common issues. Let’s explore why these valves are vital for maintaining a balanced refrigeration cycle.

What is a Thermostatic Expansion Valve?
A Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) is a device used in HVAC and refrigeration systems to regulate the flow of refrigerant entering the evaporator, ensuring that it matches the system’s cooling load. The TXV works by sensing temperature and pressure, adjusting the amount of refrigerant that flows through it based on these factors. This helps maintain efficient cooling performance and prevents issues like compressor overload and evaporator flooding.
Key Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Typical Values / Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Internally Equalized / Externally Equalized |
| Refrigerants Supported | R-22, R-134a, R-410A, R-404A, R-407C, R-32, etc. |
| Capacity Range | 0.5 TR to 100+ TR (Tons of Refrigeration) |
| Superheat Setting (Factory) | 5–7°C (Adjustable via valve stem) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +10°C (Evaporator temperature) |
| Maximum Operating Pressure | Up to 680 psi (depends on refrigerant type and design) |
| Body Material | Brass, Stainless Steel, or Copper Alloy |
| Inlet/Outlet Connection Sizes | 1/4” to 1-5/8” (ODF or SAE flare) |
| Sensing Bulb Type | Gas-charged, cross-charged, liquid-charged (depending on application) |
| Equalizer Connection | 1/4″ SAE flare for externally equalized valves |
| Orifice Size | Numbered sizes (e.g., 0.5 to 15 or A to Z) to match system capacity |
⚙️ Major Components
-
Valve Body – Contains inlet/outlet ports and houses the seat/orifice.
-
Power Element (Diaphragm) – Responds to bulb pressure.
-
Sensing Bulb – Attached to the evaporator outlet to sense superheat.
-
Capillary Tube – Connects bulb to diaphragm chamber.
-
Spring Assembly – Balances pressure forces to control valve opening.
-
Adjusting Stem – Used to fine-tune superheat setting.
Working Principle of Thermostatic Expansion Valve
How does TXV work?
The TXV controls the refrigerant flow by responding to the temperature of the refrigerant at the evaporator outlet. It uses a sensor bulb attached to the evaporator outlet, filled with refrigerant. This bulb monitors the temperature and sends signals to the valve, which adjusts the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator to match the cooling demand. The diaphragm inside the valve moves up or down, depending on the pressure and temperature changes detected by the sensor bulb, thus controlling refrigerant flow.
Thermodynamics Involved
The TXV ensures the refrigerant reaches the evaporator in a semi-liquid, semi-gas state. As the refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air, it vaporizes. The TXV adjusts the flow to maintain optimal superheat (the temperature above the boiling point of the refrigerant), preventing liquid refrigerant from reaching the compressor, which could damage it.
1. Superheat (SH)
The most important concept in TXV control is superheat, which determines how much the valve opens or closes.
Superheat (°C)=Tbulb−Tevap\text{Superheat (°C)} = T_{\text{bulb}} – T_{\text{evap}}
-
TbulbT_{\text{bulb}}: Temperature measured by the sensing bulb at the evaporator outlet
-
TevapT_{\text{evap}}: Saturation temperature corresponding to evaporator pressure (from refrigerant tables)
2. Force Balance Equation (Main TXV Control Principle)
The valve operates based on a balance of forces:
Fbulb=Fevap+FspringF_{\text{bulb}} = F_{\text{evap}} + F_{\text{spring}}
-
Fbulb=Pbulb⋅AF_{\text{bulb}} = P_{\text{bulb}} \cdot A: Force due to pressure in the sensing bulb
-
Fevap=Pevap⋅AF_{\text{evap}} = P_{\text{evap}} \cdot A: Force due to evaporator pressure
-
Fspring=k⋅xF_{\text{spring}} = k \cdot x: Force of the adjustable spring (linear function of deflection)
-
AA: Diaphragm area
-
kk: Spring constant
-
xx: Compression of the spring
3. Refrigerant Mass Flow Rate Through TXV
This formula gives an estimate of refrigerant flow rate through the valve:
m˙=C⋅Ao⋅2⋅ρ⋅ΔP\dot{m} = C \cdot A_o \cdot \sqrt{2 \cdot \rho \cdot \Delta P}
Where:
-
m˙\dot{m}: Mass flow rate of refrigerant (kg/s)
-
CC: Discharge coefficient (depends on valve design)
-
AoA_o: Orifice area (m²)
-
ρ\rho: Density of refrigerant (kg/m³)
-
ΔP=Pinlet−Pevap\Delta P = P_{\text{inlet}} – P_{\text{evap}}: Pressure drop across the valve (Pa)
4. Heat Transfer in Evaporator (Linked to TXV)
Q=m˙⋅hfgQ = \dot{m} \cdot h_{fg}
-
QQ: Heat absorbed in the evaporator (W)
-
m˙\dot{m}: Refrigerant mass flow rate
-
hfgh_{fg}: Latent heat of vaporization for refrigerant (kJ/kg)
This ties the valve performance directly to cooling capacity.
5. TXV Valve Opening vs Superheat
The valve orifice area (and thus flow) increases as actual superheat exceeds setpoint.
Types of Expansion Valves
Thermostatic Expansion Valve vs. Other Expansion Valves
TXVs are often compared to other expansion devices like capillary tubes, automatic expansion valves (AEV), and electronic expansion valves (EEV). Unlike capillary tubes, TXVs respond dynamically to changing loads, making them more efficient. While AEVs only regulate based on pressure, TXVs account for both temperature and pressure, ensuring better control. EEVs, although highly precise, are more expensive and complex than TXVs.

Types of Thermostatic Expansion Valves
- Externally Equalized TXV: These valves are designed for systems with large pressure drops across the evaporator. They have a second port for pressure equalization, ensuring proper refrigerant control.
- Internally Equalized TXV: These valves are suitable for systems with minimal pressure drops, where equalization occurs internally.
Components of a Thermostatic Expansion Valve
A TXV consists of several critical parts:
- Valve Body: The outer casing that holds all the components together.
- Power Element: This part houses the sensor bulb and diaphragm.
- Sensor Bulb: Detects the evaporator outlet temperature and helps control refrigerant flow.
- Diaphragm: Moves based on signals from the sensor bulb, adjusting refrigerant flow.
- Spring Adjuster: Sets the desired superheat level.
- Orifice: The point where the refrigerant is throttled to enter the evaporator.
Each part plays a vital role in ensuring the valve operates correctly, maintaining system efficiency and preventing issues like overfeeding or starving the evaporator.
Importance of Thermal Expansion Valves in HVAC Systems
Why Use a TXV in Air Conditioning?
TXVs improve energy efficiency by ensuring that the correct amount of refrigerant flows into the evaporator, preventing under or overfeeding. This helps in maintaining a balanced cooling process, reducing energy consumption, and enhancing overall performance. TXVs also help regulate humidity levels by ensuring the evaporator coil is adequately saturated, improving indoor air quality.
Improving Compressor Life
One of the biggest advantages of a TXV is its ability to protect the compressor. By maintaining proper superheat levels, the TXV ensures that no liquid refrigerant enters the compressor, which could cause damage or even failure. This extends the life of the compressor and reduces the need for expensive repairs or replacements.
Installation and Calibration of TXV in HVAC System
Installation Process
Installing a TXV requires careful attention to detail.
- Mount the valve on the liquid line leading to the evaporator.
- Secure the sensor bulb on the suction line close to the evaporator outlet.
- Ensure all connections are tight and leak-free.
- Verify proper insulation of the sensor bulb to avoid false temperature readings.
Calibration and Adjustment
After installation, the TXV may need to be calibrated to ensure the correct superheat setting. The spring inside the valve can be adjusted to fine-tune refrigerant flow. Superheat should typically be between 8-12°F, but it may vary based on the specific system requirements.

Common Problems and Troubleshooting Tips
Frequent Issues with TXVs
Some of the common issues faced by TXVs include:
- Sticking Valve: The valve may get stuck due to debris or moisture inside the system.
- Clogging: Dirt or debris can clog the valve, reducing its effectiveness.
- Improper Sensing: If the sensor bulb is not correctly placed, it may send incorrect signals to the valve.
- Superheat Issues: Incorrect superheat settings can lead to improper refrigerant flow, causing inefficient cooling.
Troubleshooting Guide
- Check for leaks around the TXV connections.
- Clean the valve to ensure no debris is obstructing it.
- Recalibrate the valve if superheat settings are off.
- Inspect sensor bulb placement to ensure it’s properly installed on the suction line.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Pros of Using TXVs
- Precise Temperature Control: TXVs offer excellent control over refrigerant flow.
- Energy Efficiency: By maintaining optimal refrigerant flow, TXVs improve the efficiency of the system, reducing energy consumption.
- Prolonged Compressor Life: They help prevent liquid refrigerant from damaging the compressor, extending its life.
Cons of Using TXVs
- Higher Initial Cost: TXVs are more expensive than simple valves like capillary tubes.
- Complex Installation: Installing and calibrating TXVs require expertise and precision.
Applications of Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Commercial and Residential HVAC Systems
TXVs are widely used in both residential air conditioners and large commercial HVAC systems due to their efficiency and reliability. They ensure precise refrigerant control in home air conditioning systems, refrigerators, and even larger cooling systems in commercial buildings.
Industrial Refrigeration Systems
In industrial setups like supermarkets, cold storage facilities, and large refrigeration plants, TXVs help maintain consistent cooling temperatures and prevent spoilage of perishable goods.
Maintenance of Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Routine Maintenance Guidelines
To keep a TXV functioning optimally:
- Regularly inspect for leaks or signs of wear.
- Clean the valve and surrounding components to avoid clogging.
- Periodically check and recalibrate the superheat settings.
When to Replace a TXV
If the valve becomes too worn, clogged beyond repair, or fails to regulate refrigerant flow, it’s time for a replacement.
Latest Developments and Innovations in TXV Technology
Modern TXV Designs
Today’s TXVs have evolved, with some featuring digital controls for even greater precision in refrigerant flow. These newer models are highly responsive and can be integrated into smart HVAC systems for remote monitoring and adjustments.
Integration with Energy-Efficient Systems
With a growing focus on energy efficiency, TXVs are now an essential part of smart, energy-efficient HVAC systems, ensuring lower energy consumption while maintaining high performance.
Conclusion
The Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) is an integral component of modern HVAC systems, playing a crucial role in refrigerant control and energy efficiency. Its ability to precisely regulate refrigerant flow, improve system performance, and protect vital components like the compressor makes it a valuable addition to any cooling system. For homeowners and businesses alike, ensuring the proper installation, calibration, and maintenance of a TXV can result in significant energy savings and extended system longevity.